
News -
Telenor Connexion releases: A guide to mobile IoT: How to choose between LTE-M and NB-IoT for global deployments
Today Telenor Connexion releases a whitepaper that explains the differences between the mobile LTE-M and NB-IoT technologies and for which use cases these are relevant. The intention is to help global enterprises to make the right selection for new IoT solutions and in the migration from 2G/3G to 5G.
The whitepaper guides enterprises in the choice between LTE-M and NB-IoT, often referred to as mobile IoT. Both technologies are internationally available today and future-proof as part of the 4G and 5G standards.
The paper both addresses enterprises looking to develop new IoT solutions as well as enterprises migrating their solutions to future-proof technology as 2G and 3G networks are being gradually sunset. With the introduction of mobile IoT, for the first time it is possible to use mobile networks designed already from the start to connect things rather than people.
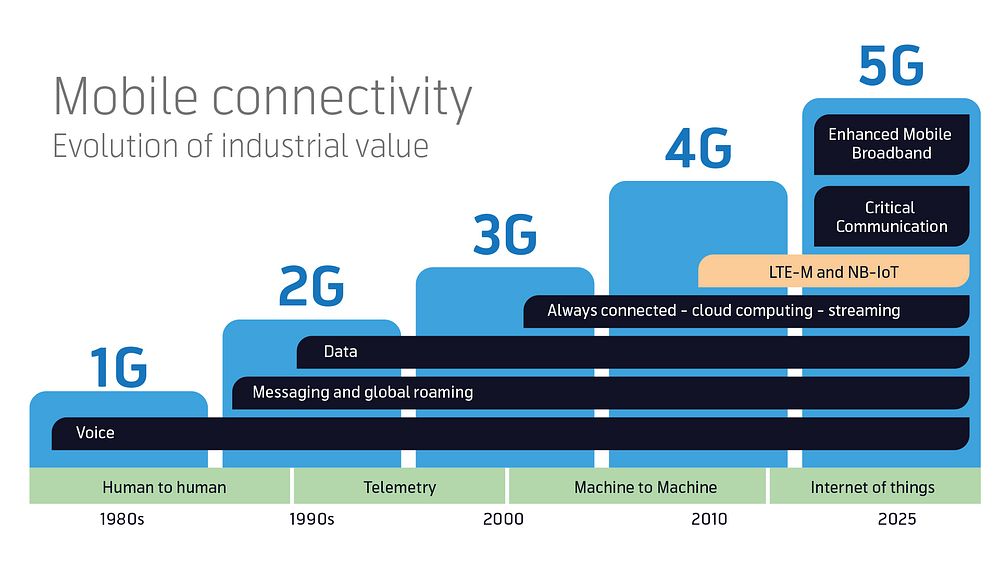
Mobile connectivity, evolution of industrial value.
Mobile IoT opens up new use cases through improved coverage, longer lasting batteries and/or lower device cost. For most international IoT solutions, LTE-M will be the preferred connectivity standard, as it is expected to become globally available faster and to be more straightforward to develop lifecycle management applications for. NB-IoT may be the better choice for some applications, e.g., for very large-scale sensor networks where the technical and international coverage requirements are known at time of deployment.
Jelte Jansons, Product Manager Managed Connectivity at Telenor Connexion says “We believe that LTE-M will be the natural choice for international IoT deployments as it is future-proof and is a natural evolution of existing 2G/3G based solutions. It can also be used with a global SIM card already today.”
The whitepaper: A guide to mobile IoT: How to choose between LTE-M and NB-IoT for global deployments can be downloaded at telenorconnexion.com or in the resource link.


